Debridement: A Crucial Medical Procedure for Wound Healing
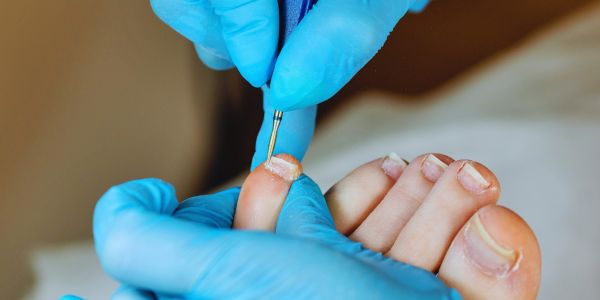
Debridement is a critical medical procedure used in wound care and management. It involves the removal of dead, damaged, or infected tissue from a wound, allowing the body to initiate the healing process effectively. This procedure plays a vital role in preventing infection, promoting tissue regeneration, and expediting the overall healing of wounds. In this article, we will delve into the various aspects of debridement, its significance in healthcare, and the different methods employed in this essential medical practice.
The Importance of Debridement
Wound healing is a complex biological process that the body initiates as a response to injury. However, in cases where wounds are contaminated with dead or infected tissue, foreign debris, or biofilms, the natural healing process can be hindered. This is where debridement becomes indispensable. By removing these impediments, debridement creates a favorable environment for the body to heal itself efficiently.
Methods of Debridement
Several methods of debridement are employed in clinical practice, each with its unique advantages and considerations. These methods include:
Surgical Debridement: This involves the use of a scalpel or surgical instruments to physically excise necrotic or infected tissue from the wound. Surgical debridement is precise and effective, but it is generally reserved for severe cases.
Sharp Debridement: Similar to surgical debridement, sharp debridement is a manual process that employs scissors, forceps, or scalpels to remove non-viable tissue. It is often performed by trained healthcare professionals and offers a targeted approach to tissue removal.
Mechanical Debridement: This method involves the use of mechanical forces, such as whirlpool therapy or high-pressure irrigation, to dislodge and remove dead tissue and debris from the wound. It is less invasive than surgical debridement but may require multiple sessions.
Enzymatic Debridement: Enzymatic agents are applied topically to the wound, where they break down necrotic tissue and debris. Enzymatic debridement is less painful than other methods and is particularly useful for wounds in sensitive areas.
Autolytic Debridement: Autolytic debridement utilizes the body’s natural processes to break down necrotic tissue. It involves the application of dressings that create a moist wound environment, allowing the body’s enzymes and immune cells to gradually remove dead tissue.
Biological Debridement: Maggot therapy, a form of biological debridement, uses sterile fly larvae to consume dead tissue while leaving healthy tissue intact. This method has gained popularity in recent years due to its effectiveness in certain cases.
Choosing the appropriate debridement method depends on factors such as the type and location of the wound, the patient’s overall health, and the healthcare provider’s expertise.
Conclusion
Debridement is a fundamental component of wound care, crucial for ensuring the proper healing of wounds. It removes obstacles that hinder the body’s natural healing processes, reduces the risk of infection, and promotes tissue regeneration. Healthcare professionals must carefully assess wounds to determine the most suitable debridement method for each case, considering the patient’s overall health and specific needs. In an era of advanced medical techniques and technologies, debridement remains a simple yet essential procedure that contributes significantly to patients’ well-being and recovery. Its continued use and refinement play a vital role in modern healthcare, enhancing our ability to treat wounds effectively and improve patient outcomes.
STEP 1:
Access Nail & Foot Care FREE Report
Enter Your Correct Details Below To Access The FREE Report

Fill in the Form
Please input a valid name & email to receive this amazing opportunity.

Check Your Email
Got to your email provider to find the email from MetropolitanNailSalon.com

Click Confirm Your Subscription
Find confirm your subscription to access the FREE checklist.
Services We Offer:
Manicure Services

Mani-Pedi Treatments

Pedicure Services
Callus Care
Diabetic Pedicures
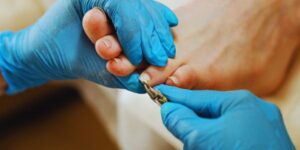
Debridement

Scheduled an Appointment Today for Professional Services!

- Welcome to MetropolitanNailSalon.com – Professional Care for Your Hands & Feet
- Get Quality Care from A Professional Expert
- Keep Your Hands & Feet Healthy with Regular Routine Visits
- Ensure Safety and Hygienic Practices with Our Advanced Sterilization
- Feel Confident in Your Hand and foot Health After Each Visit
- Experience Lasting Relief from Pain and Discomfort with Toenail Debridement Treatments
920 Bob Wallace Ave SW Suite 325 Huntsville, Alabama 35801